AttributionModels
Google confirms sunset details for 4 attribution models in Ads and Analytics
In a significant move towards refining advertising measurement and attribution, Google has announced the retirement of four attribution models within its Ads and Analytics platforms. This development signals a strategic shift towards more sophisticated and comprehensive attribution methodologies that provide a clearer understanding of user behavior and conversion paths. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of the attribution models slated for sunset, and explore the implications and potential benefits for advertisers.
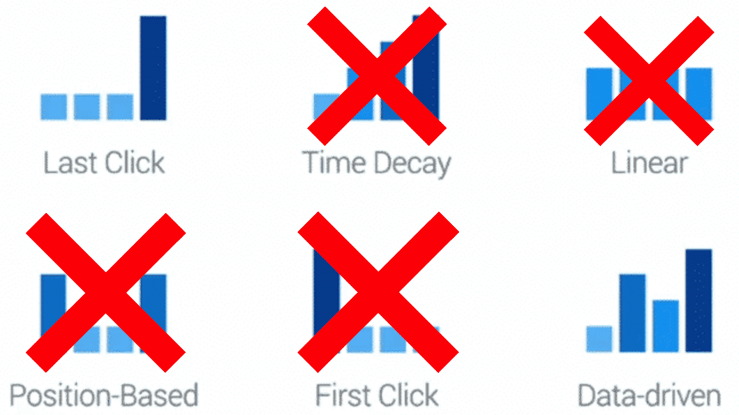
The Attribution Models Facing Sunset
1. Last Non-Direct Click:
The Last Non-Direct Click attribution model has long been a staple in digital advertising analytics. It attributes a conversion solely to the last channel a user interacted with before converting, excluding direct traffic. This model’s simplicity has made it accessible for advertisers, but it also comes with limitations in providing a holistic view of the customer journey.
2. Last Google Ads Click:
Similar to Last Non-Direct Click, the Last Google Ads Click model attributes conversions specifically to the last click on a Google Ads ad. This model has been instrumental in understanding the direct impact of paid advertising efforts. However, as the digital landscape evolves, there is a growing recognition of the need for more nuanced attribution models that consider the entire user journey.
3. First Interaction:
The First Interaction model credits the conversion entirely to the first channel the user interacted with. While useful in identifying the initial touchpoint that led to a conversion, it offers a simplified view of attribution that may not capture the complexity of modern consumer behavior.
4. Linear:
The Linear attribution model distributes conversion credit evenly across all touchpoints in the user’s journey. While this approach acknowledges the influence of multiple touchpoints, it does not differentiate between the varying levels of impact each interaction may have had.
Implications for Advertisers
1. Shift Towards Comprehensive Attribution:
The retirement of these four attribution models indicates a broader industry trend towards embracing more comprehensive attribution methodologies. Advertisers are recognizing the need to understand the entire customer journey, from initial touchpoints to final conversions.
2. Encouraging Adoption of Advanced Models:
As Google sunsets these models, advertisers are encouraged to explore and adopt more sophisticated attribution models, such as Time Decay, Position-Based, or custom attribution models tailored to their specific business needs. These models provide a more nuanced understanding of how different touchpoints contribute to conversions.
3. Enhanced Insights and Decision-Making:
Advanced attribution models offer advertisers deeper insights into user behavior, allowing them to make more informed decisions about budget allocation, channel optimization, and content strategy. This shift ultimately empowers advertisers to maximize the effectiveness of their advertising efforts.
4. Alignment with Evolving Consumer Behavior:
Modern consumers interact with brands across a multitude of touchpoints, both online and offline. Sophisticated attribution models better reflect this complexity, providing a more accurate representation of the customer journey and the various factors that influence purchasing decisions.
5. Preparing for the Future of Digital Advertising:
As the digital advertising landscape continues to evolve, advertisers must be agile in adapting to new measurement and attribution methodologies. Embracing advanced attribution models positions advertisers to stay ahead of industry trends and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Google’s decision to sunset four attribution models in Ads and Analytics represents a strategic move towards more advanced and comprehensive attribution methodologies. While this shift may require an adjustment period for advertisers, it ultimately reflects a commitment to providing deeper insights into user behavior and more accurate measurement of advertising effectiveness. Advertisers who embrace these changes and explore advanced attribution models are poised to thrive in the evolving landscape of digital advertising.