Pay Per Click
Understanding Keyword Research and Match Types in Digital Marketing
Introduction
Keyword research is a fundamental aspect of any successful digital marketing campaign. It involves identifying and selecting specific words or phrases that potential customers might use when searching for products or services online. Match types play a crucial role in how these keywords are utilized in paid advertising campaigns. In this article, we’ll explore the significance of keyword research and delve into the various match types used in digital marketing.
I. The Importance of Keyword Research
Keyword research forms the bedrock of a successful digital marketing strategy. It allows marketers to understand the language and terminology their target audience uses when searching for products or services online. By identifying high-performing keywords, businesses can optimize their content, website, and advertising efforts to align with user intent, thereby increasing visibility and driving relevant traffic.
II. Types of Keywords
1. Short-Tail Keywords:
– Short and general search queries, usually one to three words long. They have high search volumes but may be less specific. Example: “running shoes.”
2. Long-Tail Keywords:
– Longer, more specific phrases that are typically four or more words long. They have lower search volumes but are highly targeted. Example: “best running shoes for marathons.”
3. Branded Keywords:
– Keywords containing the brand name or variations of it. Example: “Nike running shoes.”
4. Non-Branded Keywords:
– Keywords that do not contain the brand name. Example: “high-performance running shoes.”
III. Match Types in Paid Advertising
Match types dictate how closely a keyword in a paid advertising campaign must match a user’s search query for an ad to be triggered. There are four main match types:
1. Exact Match:
– Ads are triggered when the search query precisely matches the keyword. It provides the highest level of control but may have lower reach.
2. Phrase Match:
– Ads are triggered when the search query contains the keyword in the exact order, possibly with additional words before or after. It offers a balance between control and reach.
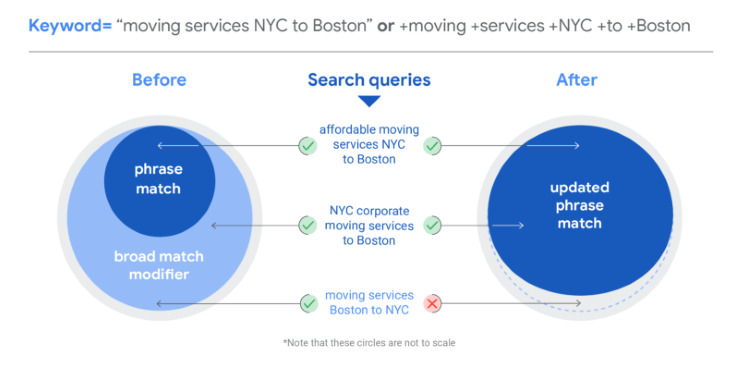
3. Broad Match:
– Ads are triggered by a wide range of variations and related searches, including synonyms, misspellings, and related terms. It provides the highest reach but may be less targeted.
4. Broad Match Modifier:
– Ads are triggered when the search query includes the modified term or close variations. It offers more control than broad matches but still allows for a wide range of related searches.
IV. Utilizing Match Types for Optimal Results
Selecting the appropriate match type depends on campaign goals and budget considerations. A balanced approach often involves a combination of match types to achieve the desired results. For instance, exact match is ideal for highly specific keywords, while broad match can be useful for discovering new, relevant search terms.
Keyword research and match types are integral components of any effective digital marketing strategy. By understanding how users search and tailoring ad campaigns accordingly, businesses can increase their online visibility and attract the right audience. A thoughtful approach to keyword selection and match type implementation can lead to higher click-through rates, improved conversion rates, and ultimately, greater success in the digital marketplace.
PPC Guide: Keyword research and match types
Creating a successful Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising campaign involves effective keyword research and understanding match types. Here’s a guide to help you with PPC keyword research and match types:
1. Keyword Research:
a. Start with a List:
– Begin by brainstorming a list of keywords relevant to your product, service, or business. Think about what potential customers might search for when looking for your offerings.
b. Use Keyword Research Tools:
– Utilize keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Moz to expand your list and identify relevant keywords.
– These tools provide data on search volume, competition, and related keywords.
c. Focus on Long-Tail Keywords:
– Long-tail keywords are specific, often longer phrases that target a more niche audience.
– They can be less competitive and lead to more qualified clicks.
d. Competitive Analysis:
– Analyze competitors’ ads and keywords to discover additional keywords you might have missed.
e. Consider User Intent:
– Group keywords by user intent: informational, navigational, or transactional.
– Tailor your ad copy and landing pages to match user intent.
2. Match Types:
Match types determine how closely a user’s search query must match your chosen keywords for your ads to appear. There are typically four match types in PPC advertising:
a. Broad Match:
– Ads may appear for a wide range of related queries, including synonyms, misspellings, and variations.
– Example: If your keyword is “running shoes,” your ad might appear for “athletic footwear.”
b. Broad Match Modifier:
– Allows you to specify that certain keywords must be present in the user’s query.
– Place a plus sign (+) in front of specific keywords within your keyword phrase.
– Example: “+running +shoes” ensures both “running” and “shoes” are in the query.
c. Phrase Match:
– Ads show when the user’s query contains your keyword phrase in the specified order.
– Use quotation marks to designate a phrase match keyword.
– Example: “running shoes” triggers ads for queries like “best running shoes” but not “shoes for running.”
d. Exact Match:
– Ads display only when the user’s query exactly matches your keyword.
– Enclose the keyword in brackets [ ] to designate an exact match.
– Example: [running shoes] triggers ads only for that specific query.
e. Negative Keywords:
– Add negative keywords to exclude your ads from showing for specific terms.
– This helps you filter out irrelevant traffic and improve campaign efficiency.
3. Organize Your Keywords:
a. Group Keywords Tightly:
– Organize your keywords into ad groups with tightly related keywords.
– This allows you to create highly relevant ad copy and landing pages.
b. Write Compelling Ad Copy:
– Craft ad copy that includes the keyword and speaks to the user’s intent.
– Use ad extensions to provide additional information and encourage clicks.
c. Monitor and Adjust:
– Regularly review your campaign’s performance and adjust keyword bids, match types, and negative keywords as needed.
4. Test and Optimize:
a. A/B Testing:
– Conduct A/B tests to compare different ad variations and landing pages.
– Test headlines, ad copy, and call-to-action buttons to improve conversion rates.
b. Quality Score:
– Keep an eye on your Quality Score, which affects ad position and cost.
– Improve ad relevance, landing page experience, and expected click-through rate.
c. Budget Allocation:
– Allocate your budget based on the performance of keywords and ad groups.
– Focus more budget on keywords that drive the best results.
Effective PPC keyword research and match type selection are essential for creating cost-effective campaigns that reach the right audience. Regularly analyze data, refine your strategy, and stay up-to-date with industry trends to continually improve your PPC advertising efforts.
Giving Yourself a Grade in Google Ads
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, Google Ads (formerly known as AdWords) serves as a powerful tool for businesses to reach their target audiences and achieve marketing goals. Measuring the success of a Google Ads campaign is essential, and giving yourself a grade in Google Ads involves assessing various key performance indicators (KPIs) to determine the effectiveness of your efforts. This essay delves into the process of evaluating your Google Ads performance and assigning yourself a grade based on the results.
Understanding Google Ads Performance Metrics
1. Click-Through Rate (CTR): CTR measures the ratio of clicks to impressions, indicating the percentage of users who click on your ad after viewing it.
2. Conversion Rate: Conversion rate reveals the proportion of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form, after clicking on your ad.
3. Quality Score: Quality Score reflects the relevance and quality of your ad and landing page, influencing ad position and cost-per-click (CPC).
4. Cost-Per-Click (CPC): CPC indicates the amount you pay for each click on your ad. A lower CPC often signifies efficient spending.
5. Return on Investment (ROI): ROI measures the profitability of your campaign by comparing the revenue generated to the cost of running the campaign.
6. Ad Position: Ad position reveals where your ad appears on the search results page. Higher positions tend to garner more clicks.
Evaluating Your Performance
1. Set Clear Objectives: Define your campaign objectives, whether it’s driving traffic, generating leads, or increasing sales.
2. Benchmark Against Goals: Compare your campaign’s actual performance against the goals you set initially.
3. Analyze Click and Conversion Data: Examine your CTR, conversion rate, and other engagement metrics to gauge user response to your ads.
4. Review Quality Scores: A high Quality Score indicates that your ads are relevant to users’ searches and are likely to rank higher.
5. Assess Cost Efficiency: Review your CPC and ROI to understand the cost-effectiveness of your campaign.
Assigning Yourself a Grade
1. A: Exceptional Performance: If your campaign surpasses all KPIs and achieves exceptional results, you deserve an ‘A.’
2. B: Above Average Performance: If you achieve most of your goals and your campaign performs well, but there’s room for improvement, consider a ‘B.’
3. C: Satisfactory Performance: A ‘C’ grade indicates that your campaign meets the minimum requirements but lacks significant impact.
4. D: Below Average Performance: If your campaign falls short on several KPIs and improvements are needed, a ‘D’ may be appropriate.
5. F: Poor Performance: An ‘F’ grade indicates that your campaign underperformed across the board and requires a major overhaul.
Taking Action Based on Grades
1. Leverage Successes: Analyze what worked well for your top-performing campaigns and replicate those strategies.
2. Address Weaknesses: Identify areas where your campaign underperformed and implement targeted improvements.
3. Test and Iterate: Experiment with different ad formats, targeting options, and messaging to optimize your campaign’s performance.
Giving yourself a grade in Google Ads is a strategic approach to objectively assess the success of your campaigns. By evaluating performance metrics, setting clear goals, and aligning your efforts with your objectives, you can gauge your effectiveness in reaching your target audience and achieving desired outcomes. The process of assigning yourself a grade not only helps you acknowledge your successes but also guides your path toward continuous improvement in the dynamic realm of digital marketing.
Ad Sitelinks With New Feature Of Embedded Format
Google AdWords is always experimenting with new formats, enhanced targeting, and other ways to make both Google and all its advertisers a little more money. Their most recent experiment is embedded Ad SiteLinks, which automatically link portions of your ad’s text to sub-pages inside your site.
With the embedded format of Ad Sitelinks, there are no extra lines appended to your text ad. Instead, text in your ad that exactly matches one or more of the sitelinks in your campaign will automatically be linked to that sitelink’s destination URL. With embedded sitelinks, potential customers can pick the part of your ad that applies straight to their current interests and visit the most specific page for that topic.

For example, if you sell home goods, your ad may mention that you sell appliances, furniture, and flatware. If you have separate sitelinks set up for the words “appliances,” “furniture,” and “flatware,” those words would be hyperlinked in your ad text, leading potential customers to a page for the specific part of the ad that drew their interest. These targeted destination URLs may encourage more users to click on your ad and make it easier for them to find what they’re searching for when they arrive on your site.
To show with embedded sitelinks, your campaign must be enabled for Ad Sitelinks. Also, your ad must show above the search results, and part of your ad text must accurately match one or more of your Ad Sitelinks. Additionally, embedded sitelinks will only show for ads that don’t meet one or more of the necessities for one- or two-line Ad Sitelinks.
Introducing +1 Buttons In Adwords
You can get no better recommendation than one from a friend. On the Internet, everyone can suggest content to friends using the Facebook “Like” button. Now Google also want to help you make recommendations with their new +1 button. However, Google’s button comes with a twist. It will be included within AdWords ads.
+1 is a simple idea. In order to understand how this new feature might work, let us look at an example.
When Brian signs into his Google account and see one of your ads or organic search results on Google, he can +1 it and recommend your page to the world.

The next time Brian’s friend Andrew is signed in and searching on Google and your page appears, he might see a personalized annotation letting her know that Brian +1’d it. So Brian’s +1 helps Andrew decide that your site is worth checking out.
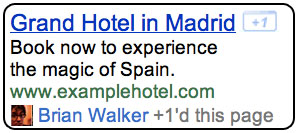
Google says that there is no strategy to use the +1 button as part of the calculation for Quality Score. However, a well-recommended ad should see a big boost in click-through-rate. You could therefore see an in-direct advantage on your Quality Score and the price you have to pay in order to bid on a particular keyword.
Currently, the +1 button is being rolled out only on Google.com. You do not have to make any changes to your account. The button will be incorporated in your ads when available. Other languages are being worked on and you can be expecting further releases to be announced soon.